Why Stellar Parallax does not prove the Earth's motion and why star distance is likely wrong.
Another false claim by 'The Science'. Stellar parallax probably does not even exist and if that is true, planetary distances are false and mostly everything emitted by NASA is wrong.

In a previous post we discussed the many experiments which could find no movement of the Earth through the ‘aether’ (now called ‘dark matter’), or Einstein’s fictitious ‘vacuum’ of space (now defined as a ‘lack of energy’). These are never taught. In schools we are told that the stellar ‘parallax’ ‘proved’ that the Earth is moving. The German astronomer Bessel in 1838, is usually credited with this ‘discovery’. It is logical to maybe pause and summarise why such claims regarding parallax are also false.
Weltanschauung
Geo-centrists from the time of Tycho Brahe, had referenced the lack of a parallax to prove immobility. There is still a lack of parallax today, given how small the effect is, how negative parallax is as common as ‘positive parallax’, how few stars are affected and how different non-Copernican models can explain such an effect (below).
We should keep in mind a few things. The first is that the confused Copernicus whose effort was largely philosophical, not mechanical, combined different models including the Platonic and Pythagorean, to justify heliocentricity. He offered no proofs, his book ‘The Revolutions’ being infilled with plagiarised ancient Greek astronomical tables from Rhodes and Halicarnassus.
How is it possible that after some 1 trillion miles of Earth travel in ‘space’, ancient astrological maps would still be applicable to someone in the 16th century? Never discussed.
A simple reason why parallax failed to convince anyone is that such ‘evidence’ does not support Copernicanism. The proof for this statement is that by the 1890s, Relativity was the only possible recourse left for Copernicans to support heliocentricity. In other words, if parallax was so convincing and definitive a proof for Copernicanism (or Foucault’s ridiculous pendulum experiment), that would have been that.
What is it?
A standard definition of a stellar parallax is:
Parallax is the apparent displacement of an object because of a change in the observer's point of view.
This concept is of course central to the theory of Relativity which has been well savaged in other posts. A parallax is used to measure the distance to a star. This is where the ’93 million miles’ distance to the Sun comes from. If you use Euclidean maths, you will derive a figure in the low millions at best.
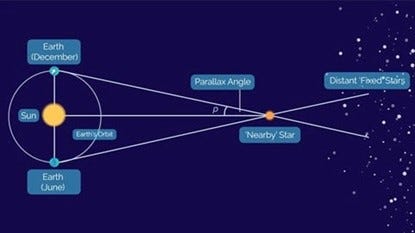
In the heliocentric system, parallax is said to occur when from one side of the Earth’s orbit, we view 2 stars on January 1 at the same time in a telescope. One star is close to us and the other star appears to be far away. Let’s say that the two stars we view on January 1 are aligned vertically in the same plane, that is, one star is at a higher position in our telescope lens than the other, but both are on the same vertical line (Ostlie and Carrol, pp. 57–59).
Six months later we look at the same two stars on July 1. If ‘parallax’ is demonstrated, we will see that the stars are not in a vertical alignment any longer. There has been a shift in the background (right hand side of above diagram). Assuming the Earth has orbited the Sun in a counterclockwise direction, the nearer star appears to have shifted to the right. This is because, in the interval of six months, one has looked at the two stars from two separate locations that are 186 million miles apart (the diameter of the Earth’s orbit). Surely things must change over 6 months when viewing a star if we are travelling at 60.000 miles per hour!
Since stellar parallax can now be detected among a select few stars, most astronomers who are Copernicans, interpret the phenomenon as proof for the Earth’s movement around the Sun. This is absurd and tautological. You must first prove the mechanical movement (light interferometer experiments which have all failed for example), and then assess star locations over time. You can’t jumble up your ‘axioms’ and then use circular logic to support your ‘apriori’ conclusion.
It proves nothing
Relativity was necessary to mathematically ‘prove’ Copernicanism because most 19th physicists understood that the stellar parallax proves nothing. Other models including the Tychonic explain the observed phenomena just as well if not better. The ‘fringe’ effect of stellar parallax is also so small, that it is meaningless.
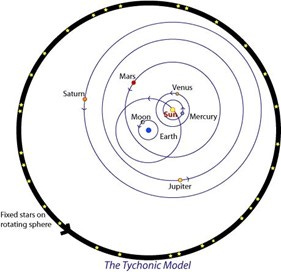
In the Tychonic system, the stars are centred on the Sun, which is also true in the heliocentric system. The only difference is that within the geocentric model the Earth is fixed in space, while both the Sun and stars revolve around the Earth. Given this fact, there can be no difference in the observed phenomena between helio-or geo-centricity.
Using the Tychonic model if we view 2 stars in December, they are in vertical alignment. When we look at these same two stars again in June, the nearer star will appear to have shifted to the right of the farther star, and it will do so at the same precise angle as in the heliocentric model.
This equivalence of the geocentric parallax with the heliocentric parallax is to be expected. Based on geometrical reciprocity, the two systems must be equal on all counts, confirmed by Mach and his disciple Einstein (see below). The only difference is that in the heliocentric model the Earth is moving, and the stars are fixed, while in the Tychonic or geo-helio-centric model the Earth is fixed, and the stars are moving. Everything else is the same. But no one is told this.
We can see the equivalence when we look at heliocentricity side by side with the Tychonic model. In the diagram below the heliocentric parallax is on the left, the geocentric on the right.
In the heliocentric model, the Earth is at the 11:00 o’clock position and is moving counterclockwise. In the geocentric model, the Sun is at the 5:00 o’clock position and moving counterclockwise with the stars. The white lines converge at the Earth and form the parallax angle. In both models the parallax angle is the same and the views from the Earth (top of both sides) will be the same.
Kepler and no parallax
“For among the most powerful causes of visiting Tycho was this also, that I might learn the truer proportions of the deviations [of the planets] from him, by which I might examine both my Cosmic Mystery and The Harmony of the World. For these a priori speculations ought not to impinge on clear experience: but with it be reconciled” (Kepler, in Heavenly Intrigue, p. 154, Gilders).
Kepler who likely killed Brahe, could easily have turned his geometric and algebraic skills to ‘prove’ Tychonism. Kepler was motivated by the lack of a parallax (Brahe’s complaint), Copernicus’ incorrect circular orbits, elucidate why and how the Earth rotated around the Sun (magnetism for Kepler, gravity for Newton), and by his desire to usurp the great man himself by offering some intelligible support for heliocentricity.
Mach, Einstein and Equivalency
Mach, Einstein/Einstotle, Hoyle and many other philosopher-physicists have maintained that there is a kinematical and dynamical equivalence between the heliocentric and Tychonic-geocentric systems (Barbour, 2010). There is, however, a difference between the two if we view motion. In the neo-Tychonic system, there is an underlying key assumption that the orbits of distant masses move around the Earth and are synchronized with the Sun’s orbit.
To prove this the motion of the Sun and Mars have been analysed, with the conclusion that an accelerated motion of the Universe as a whole, could generate a ‘pseudo-potential’ that not only explains the origin of the pseudo-forces or the forces that Newton could not identify (Coriolis, Euler, centrifugal), but also the very motion of the celestial bodies as seen from a static Earth (Popov, 34, 383).
This is evidential proof to support the Tychonian view and explanation of the parallax. If these claims are correct, then the stellar parallax is more easily explained by the neo-Tychonic model than by Copernicanism. In any case, it is obvious that the stellar parallax, which is based on a few stars and their displacement throughout the year, does not prove heliocentricity.
Distant Starlight
The entire basis of the the ‘parallax’ is the ‘distant starlight’ problem which in reality does not exist. Simply put, light speed in space is far different than on Earth due to many factors including but not limited to gravity. Assumptions inform the calculations of of starlight and distance, not empirical evidence.
If we turn the Big Bang on its head (it is certainly wrong as many posts here outline) and move from Black Holes of singularity and beyond measureable gravity density to White Holes, there is nothing in ‘standard science’ to deny the claim that if the creative genesis of the universe erupted from a White Hole, than the ‘escape velocity’ of matter and space, along with light speed and time as we understand it would be incomprehensibly and incalculably faster and younger. This means that cosmic time is vastly inflated.
The acceptance of Riemannian space (extended Euclidean space) allows us to reject Einstein’s relativity and to keep all the ordinary ideas of time and all the ideas of Euclidean space out to a distance of a few light years. Astronomical space remains Euclidean for material bodies, but light is considered to travel in Riemannian space. In this way the time required for light to reach us from the most distant stars is only 15 years (Moon p. 635) (the author is not clear about the 15 years but the path of logic is sound).
Ineluctably this would indicate that there is no ‘distant starlight’ issue. Further, many posts on here outline why Redshifting does not infer long age, but rather the opposite. Other posts discuss why the ‘invariant’ speed of light is wrong. The Big Bang itself claims that post eruption, the speed of light must have been up to 1000x faster than the claimed speed of light. Einstotle’s time dilation infers that cosmic time is far different and incompatible with Earth time. All this conspires against stellar aberration.
(Big Bang) Meaning, by time 10^-34 seconds have passed, the Universe is around 1000 times its initial size; by time 10^-33 seconds have passed, the Universe is around 10³⁰ (or 1000¹⁰) times its initial size; by time 10^-32 seconds have passed, the Universe is around 10³⁰⁰ times its initial size, and so on. Exponential isn’t so powerful because it’s fast; it’s so powerful because it’s relentless.
If we just accept the above, this declaration means that light speed is variant and varies by time (‘acceleration’) and space (JWT data is clear that the ‘expansion’ rate of space is variable). The distant starlight problem is now only a problem for the ‘standard model’ and this is called the ‘horizon problem’.
Negative Parallax
For centuries observational astronomers have detected nearby stars exhibiting a negative parallax. This means that nearby stars are regularly observed to drift in the opposite direction the Copernican model predicts. Such facts are rarely discussed of course. The distribution between positive and negative parallax observations is roughly equal (~29%, 25%). In fact hundreds of thousands of negative stellar parallaxes have been viewed.
This phenomenon was well known in the 19th century. In 1878, the famous Canadian astronomer Simon Newcomb briefly commented on the negative parallax issue, suggesting that “such a paradoxical result can arise only from errors of observation.” No Simon. It results from assuming that we on Earth are moving counter clockwise or left to right it viewed 2-dimensionally through space. Assumptions and tautologies Simon.
‘The Science’ cannot explain negative stellar parallax, so it prefers to ignore such observations.
Miniscule
Let’s look at it from the Copernican view. The heliocentric system has the same miniscule amount of parallax daily. By the time the Earth rotates in one day and a second night sky appears, the Earth has moved 1/182.5th of its semi-annual annual orbit, and the viewing angle for two stars (one star closer to Earth and the other farther away) has changed and will cause a very slight parallax – the same parallax that appears in the geocentric system.
But since this parallax is so small, we have no instruments that can detect it. Again, we know it only in theory pace the quote at the beginning of this post. The incidence of parallax is therefore so small as to be meaningless. If we add in the non-existent problem of ‘starlight’, and negative parallaxes, we are left with nothing.
Is there really a positive parallax? The author, based on his own experiments and observations expresses some strong reservations. As with ‘viruses’, electrons or neutrinos, did we really ‘discover’ a parallax, or have Sun worshipping disciples simply invented it? How then to explain the negative parallax phenomena?
The evidence for any parallax is thin indeed. I would not be resting my theory on such disputable claims.
Bottom Line
Stellar parallax, if it does really exist which is doubtful, does not prove heliocentrism. Heliocentricity might be correct. But you need to prove it. We can list the reasons why this statement is important.
1. There is no kinematical, mathematical or observational reason why the Tychonic system is incorrect. Back to worldviews, philosophies and man’s place in the cosmos.
2. The ‘distant starlight’ problem does not exist and this is the entire basis of ‘parallax’.
3. The phenomena of ‘negative parallax’ cancels out ‘positive parallax’.
4. If there is no stellar parallax (the author’s view), then all distances to the Sun, the planets and stars, based largely on Bessel’s 19th century observations, are wrong. Imagine the implosion of worldviews and scientific theories around the world! Everything you are told by NASA (not a space agency) would be wrong.
5. The fact that parallax failed as a proof for Copernicanism is evident by the flurry of light and water measurements during the last half of the 19th century. When these efforts also ignominiously failed ‘The Science’ was in a panic. This is why Relativity was constructed, and this fact is never taught.
6. Relativity itself is wrong and cannot explain the macro universe and is incompatible with quantum mechanics which is the basis of the ‘standard model’.
Yet Relativity is preached as fact, with its models and abstractions and this has led to an entirely new ‘weltanschauung’, a mathematical-world view, a philosophy of contrived explanations based on Cartesian dualism and Kantian mysticism, where nothing is absolute, no truth exists, and reality is optional. The not-so-brave-world of ‘modern physics’ and fantasies called ‘The Science’, all used to support the confused Copernicus and his lack of proofs for heliocentricity.
‘Stellar parallax’ is in the main just another of the magic totems and words used as ‘proof’ for heliocentricity and for ‘the standard model of the science’. As if it means anything. It means nothing.
All hail.
n.b. In the next post we will discuss stellar aberration, which was the first reported proof of heliocentricity, some 80-200 years after Copernicus (Pieroni, friend of Kepler and Galileo, may have reported stellar aberration in the early 17th century). When the Church asked Galileo for proof in the early 17th century, this is what it meant. The evidential proofs for Copernicanism took hundreds of years to develop and are completely unconvincing. The Galileo myth is dealt with here.
Sources
Popov, L., 2013, “Newtonian-Machian analysis of Neo-tychonian model of planetary motions,” Eur. J. Phys., 34, 383
Ostlie, D. A., and Carrol, B. W., 2007, An Introduction to Modern Stellar Astrophysics, 2nd ed., San Francisco: Addison Wesley
Barbour, J., 2010, “The definition of Mach’s principle,” arXiv:1007.3368
Parry Moon and Domina Spencer, “Binary Stars and the Velocity of Light,” Journal of the Optical Society of America, Vol. 43, No. 8, August 1953, p. 635)





I've enjoyed finding and reading your Substack. I believe that the sun revolves around the earth because I believe it's the teaching of Scripture. So I have a question on rotation; if the earth is not rotating (spinning), how does this affect airplane flights? I'm thinking that they're basing their calculations on a supposedly spinning earth, spinning at a certain speed, and believing erroneously that this also provides the size of the earth?
This is great, thanks. But I am still a bit confused. Leaving aside the earth's supposed orbit of the sun, does the earth rotate every 24 hours or not? Is there any good evidence that the earth is actually rotating. If the earth is not rotating then we must believe that the heavens rotate about the earth and the further away a star or planet is, the faster it must be moving. Is that correct? I just read the wiki on Tycho and it seems to suggest that Tycho did not think the earth was rotating. What is your view based on the available evidence?